LAB Experimental : Intelligences artificielles – Etienne Mineur
Le grille de proportion avec ses 100 cases (équivalente chacune à 1% de ciel) a ses limites. Son calcul est approximatif seulement et ne s’adapte pas à toutes les typologies de fenêtres et d’espaces.
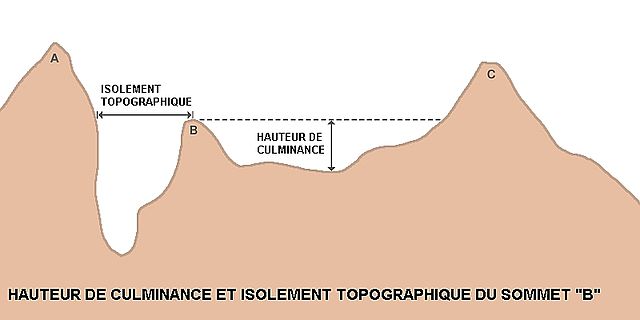
J’imagine alors un outil plus performant et précis, un boîtier de calcul automatique que l’on vient placé dans l’espace duquel on souhaite avoir la proportion de ciel. Le capteur rappel les géomètres pour faire des relevés topographiques.
Boîtier de mesure de la proportion de ciel généré par MIDJOURNEY :


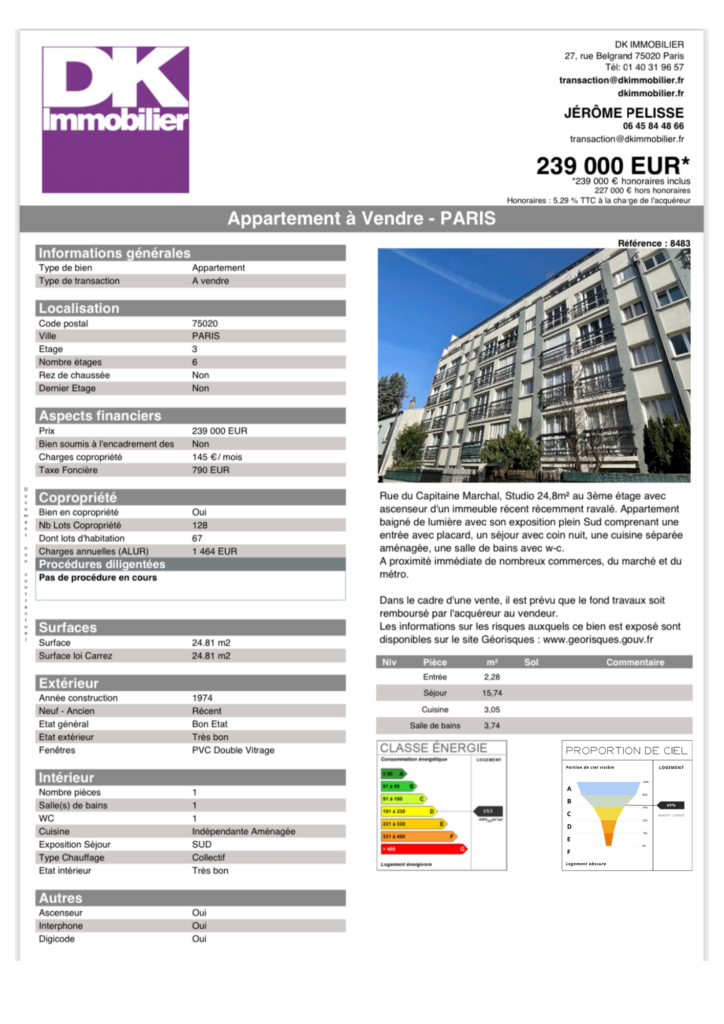
Fiche technique d’un agent immobilier avec le nouvel indicateur :
Abstract (in English )
The ‘Sky View Factor’ is a measure of how much sky you can see from a certain point. If you were on an infinite plane you would see a full half dome of sky. That would be 100% sky view factor.
As soon as something is placed on the infinite plane – trees, buildings, hills – parts of the sky are hidden. You can no longer see 100% of the sky: the Sky View Factor falls. The more things, the bigger and taller they are, the lower the SVF.
It is a measure for feeling enclosed, and will have an impact on the quality of open space.
It is quite easy to create the index for a point.
- shoot rays out from the test point
- check which hit geometry
- associate each ray with a patch of the sky dome.
- Work out the area of the sky that is visible from each point
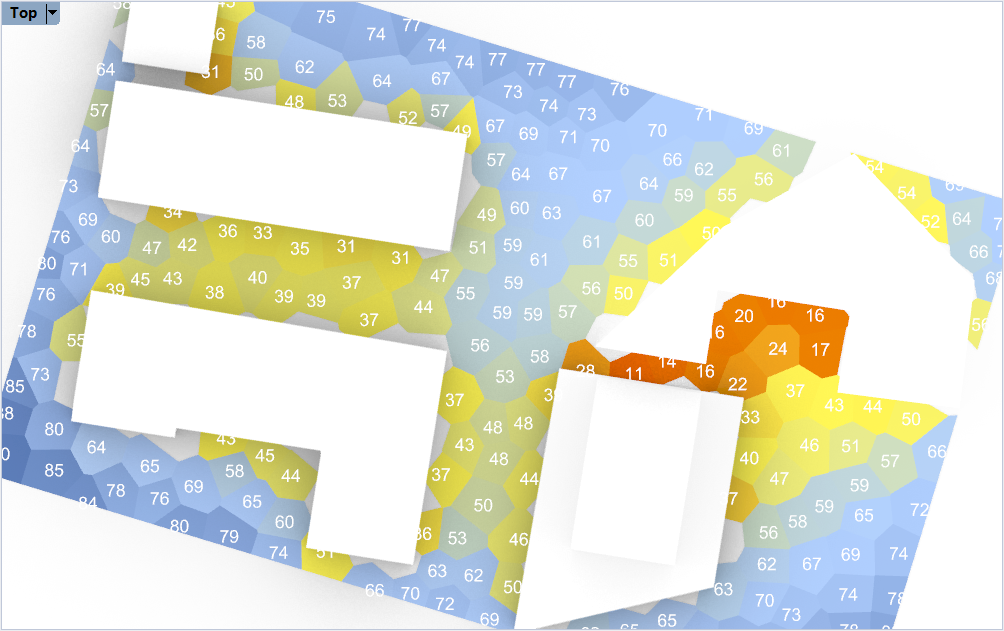
Researches :
The sky view factor (SVF) is essential to describe the urban climatology at scales below 100m. This proxy for net radiation depends on the height of the obstacles in its surroundings. The SVF was calculated from a rasterized point cloud height dataset (with 6 − 10 points per m2). The resulting SVF depends on grid-resolution, search radius and number of directions. Previous research related the diurnal maximum urban heat island (UHI) of the canopy layer to the diurnal temperature range, solar irradiance, wind speed, vegetation fraction and SVF. The goal of this study is to determine the sensitivity of the SVF and the impact on the UHI. Within the Netherlands a test area of 70km2 was selected, including: urban areas, meadows and forests. There is a high sensitivity for grid-resolution. Therefore the impact of the SVFs grid resolution on the maximum UHI is explored. Results show that the fourth largest city within the Netherlands, Utrecht, has a mean diurnal maximum UHI of 3.1 °C using a 1m SVF resolution. But, with a 3m SVF resolution the UHI is on average 0.6 °C lower. This highlights the significance of a fine grid resolution which can capture houses, alleys and trees.
La photogrammétrie au service
des archéologues et des architectes
AliceVision est un framework de vision par ordinateur et de photogrammétrie qui permet de générer un modèle 3D texturé à partir d’un ensemble non ordonné de photos.